Let's Get Started
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Questions? Find your answers here.
FAQ’s
Find the most frequently asked questions on the Visionpi Visual LED products and LED technology here for your convenience. Do you have special questions? Contact our support team directly. Alternatively attending a VISIONPI Academy course is a great way to boost your LED knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions About LED Displays & Technology
LED Display Basis
Why use led screen?
This question is most often asked in comparison to projectors and projector screens. The projected image is a reflection, not actually a light source, so the maximum brightness you can get off of a reflection is never enough in sunlight verses a LED screen. LED Screens are light-emitters, as opposed to standard projection screens which are light-reflectors. This means that the screen IS the light source, so you get brighter images and more vibrant colors. LED’s actually produce colors in a range greater than most video cameras are capable of capturing! Unlike projection screens, LED Screens are useable in bright environments such as convention centers, stages with full scenic lighting, and even the sunny outdoors.
Another question we get often is in comparison to flat panel television walls. In this scenario, several TV’s are butted together to make the wall. The first problem here, and probably most glaring, is the seams between the walls. Viewed side by side, the LED screen is one large seamless screen, where the TV panel matrix’s seams are constantly, jarringly there. It’s very hard for the brain to forget that these seams are right in the middle of the image and they are a constant distraction. Another problem with them in comparison to LED screens is their picture. The TV panels just can not produce the same amount of brightness and crispness that an LED screen can, and that’s what attracts eyes. With our ultra high resolution panels, we can achieve the same HD quality and much higher brightness and contrast than any flat panel TV wall matrix.
Another huge reason to consider LED is that outdoor LED screens are built for the weather, and can remain in service during a rainstorm. This is a huge plus for event organizers, especially in the summer when unexpected weather could develop at any time.
LED screens are getting lighter in weight and higher resolution all the time. When you partner with Neoti, we will provide the screen type that best fits your situation and budget.
HOW TO SELECT THE RIGHT LED SCREEN?
Choosing the right LED display solution for you depends on several things. You need to start by asking yourself — where will you install your LED display? Indoors or outdoors? This will help you narrow down your choices.
Then, you need to think about how big you want your LED video wall or signage to be, what kind of resolution you need, whether you want it to be mobile or fixed, and how you want to mount it.
After you answer these questions, you’ll have a better idea of what LED panel suits you best. And don’t worry, we also offer custom solutions if you have specific needs.
What is led modules?
LED modules are made up of parts that form the building blocks of video displays, message centers, and dynamic message signs. Rows of modules line together to arrange the LEDs in different variations depending on their product, market and purpose.
What is led disply resolution?
Resolution is a way of measuring how many pixels are in a given area of a digital display. Pixels are tiny dots that make up digital images, like grains of sand make up a beach. The more pixels there are in a certain space, the clearer and sharper the images can be.
Resolution is usually written as width x height, where width and height are the number of pixels along each dimension. For example, some common resolutions are:
Full HD = 1920 pixels x 1080 pixels
4K = 3840 pixels x 2160 pixels
8K = 7680 pixels x 4320 pixels
These resolutions mean that Full HD has about 2 million pixels, 4K has about 8 million pixels, and 8K has about 33 million pixels. The higher the resolution, the more detail and quality the images can have.
What is Pixel?
Pixels: The Building Blocks of Digital Images Pixels, which stands for picture elements, are tiny dots of light that make up letters, words, graphics, animations and video images on a digital display. A pixel can consist of one LED, several LEDs of the same color or several LEDs of different colors. They are the smallest units of the digital display system that can be individually controlled and turned on or off at different brightness levels.
What resolution is right for you?
There are three main categories of resolution use cases — and a real example from each.
Communication display
At about 48 to 60 pixels tall, you’ve got enough resolution to display a text-based message to your audience. Whether that’s “Free Oil Change” or “25 percent off, today only,” words are usually all you need to captivate passersby and get them to take action.
Graphic display
Moving up to 61 to 100 pixels tall puts you in a new category — one where displaying visual imagery becomes possible. Icons, logos, 3D text, and basic graphic representations of the products and services you’re promoting are all fair game.
Video display
Once you’re above 100 pixels tall, you’re in high-resolution video display territory. The content you can display here is more akin to what you’d see on your favorite streaming service. You can show video or premium images that look vivid and appealing.
HOW to check the led display specifications
When you are about to purchase an LED screen, for indoor or outdoor, advertising, retail, sport, rental & staging, or information, it is imperative to ask for, obtain, and comprehend a detailed specs sheet of the product offered.
This document must always contain a minimum number of essential features like display size with and without any possible enclosure and with an indication of the dimensions of the cabinet or module on the base of which the screen is composed:
1. graphic definition (horizontal pixels by vertical pixels),
2. PHYSICAL pixel pitch (distance between the centers of adjacent RGB dots);
3. resolution(number of pixels per square meter);
4. type of LEDs used (whether SMD or traditional);
5. brightness (in NIT, i.e. candelas per square meter, > 5000 for outdoor use);
6. IP protection rating (65 for outdoor use) and horizontal/vertical viewing angle.
To this basic information other things should be added up, all very important to understand if the model is suitable.
7. Total weight, power supply;
8. maximum/average power consumption is required to prepare well the site and plan the total investment.
How big of an LED screen can you build?
In principle, the size of the display screen can be infinite. Depends on the size of the overall resolution. The final size is best to choose a resolution ratio close to 4:3 or 16:9. Bty, budget management also need to be considered.
WHAT IS THE WARRANTY ON THE PANELS?
The warranty is 2 years parts and labor on all of our products.
Unlike most companies, we are here to make sure your displays are covered when you need them most. We cover our panels from edge to edge, pixel to pixel including all aspects of your LED tiles. Visionpi LED warrants all of our products for a period of 2 years to the original purchaser, to be free of any defects in workmanship and materials under normal use as intended by VISIONPI for the entire warranty period.
What is your payment terms?
Our payment term is T/T,20%-50% as deposit, balance before shipment.
If there is a broken lamp or other problem,how to repair it?
3% spare parts are prepared with every order (every batch), which can be replaced and repaired at any time. You can send it back to our technicians for maintenance, or we can guide you online for maintenance.
How long is your lead time?
The lead time of all the orders is about 15-30days.3-5 working days when we have stock available , And we will report all the processes to you.
LED Display Specification explain
the types of LED package DIP SMD COB
DIP
DIP stands for Dual In-line Package, which means that the LED chips are packaged in a rectangular shape with two parallel rows of pins. This makes the LED chips more durable and resistant to water and dust. DIP LED display also has a higher brightness than other types of LED displays, such as SMD (Surface Mount Device) or COB (Chip On Board). This is because the DIP LED display uses three separate red, green, and blue LED chips for each pixel, while SMD and COB use one integrated RGB LED chip for each pixel. The separate LED chips can produce more light and consume less power than the integrated ones.
That’s why the DIP LED display is ideal for outdoor applications, where brightness and durability are important factors. DIP LED display can withstand harsh weather conditions and provide clear visibility even under direct sunlight. However, DIP LED display also has some disadvantages, such as lower resolution, larger pixel pitch, and higher cost than SMD or COB LED displays. Therefore, DIP LED display may not be suitable for indoor applications or applications that require high-definition images.
SMD
SMD stands for Surface Mounted Diode — a widely used type of LED diode today. A SMD is an improvement in technology compared to Standard LED diodes in the sense that it’s mounted directly flat against the circuit board. Standard LEDs, on the other hand, require wire leads to hold them in place on the circuit board.
COB
COB is an abbreviation for Chip On Board. This is a type of LED that is formed by bonding multiple LED chips to create a single module. The advantages to the COB technology is a brighter display with fewer components to deal with in the housing, which helps lower the heat generated and create a more energy efficient display overall.
Brightness (nits) of led display
Nits are a way of measuring how bright a screen is. The more nits a screen has, the more light it can produce. Different types of screens have different ranges of nits. For example, indoor LED screens are usually at 600-1000 nits, while outdoor LED screens need to be at least 4500-6000 nits to be visible in the sun. in some area (Middle east,Africa, South America) it requires 7500-1000nits
Before, TVs could only reach up to 500 nits, but now they can go much higher. Projectors, on the other hand, are measured in lumens, which are not as bright as nits. That’s why LED screens have a better picture quality than projectors.
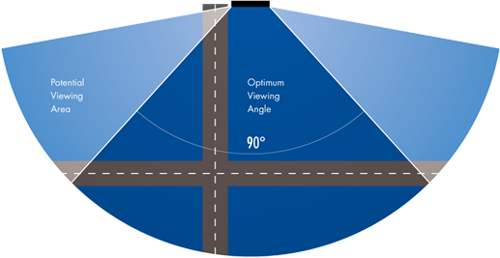
What is the viewing angle of the screens?
All of our LED screens have at least a wide 120-degree viewing angle. This means that the image still looks good and readable for 60° in each direction of the front of the screen left and right, whereas 90° would be completely sideways of the image. Some of our products have a very wide 140° viewing angle! This is all a fancy way of saying that LED screens in general have a very wide-angle viewing ability, so as long as your crowd is in front of the screen, even on the sides, they’ll be able to see the image clearly. It’s one of the most surprisingly pleasant features of LED screens to first-time LED clients.
What is the viewing distance of led screens?
The picture quality or the optimum viewing experience is maintained at the optimal viewing distance. This is the distance where you can see the LED screen clearly without noticing individual pixels.
If you move too close to the LED screen and go below the minimum viewing distance, the picture will look blurry and pixelated. This means you can see the separate pixels that make up the LED display.
The pixel pitch of the LED display and the size of your room or space are important factors to consider when finding the best viewing distance for your application.
The pixel pitch is the distance between two adjacent pixels on the LED display. The smaller the pixel pitch, the shorter the minimum viewing distance.
If your room is small, you should choose LED displays with smaller pixel pitch. This way, you can enjoy a clear and sharp picture even at a close distance.
![]()
Can we watch 16x9 video on a 4x3 screen?
You absolutely can watch a standard sized video on a non-standard sized screen, you just have to make some concessions. The first option is to letterbox the image, which means there will be black bars on the top and bottom of the screen, not unlike watching a wide-screen DVD on a regular television.
Another option, if you want to use all of the screen, is to zoom the image in, which will fill up the entire screen, but cut off the extreme sides of the image. Many times this is the option we use for video heavy content or live video applications. Typically, as long as the camera operators are aware of the 4X3 aspect ratio, they will adjust their shots accordingly to keep the subject toward the center of the shot and away from the extreme side edges.
The second option is to make the picture anamorphic, which squeezes the image to fit the screen. Sometimes this is preferred because it allows the entire image to be on the screen and take up the whole screen without letterboxing. The trade-off here is that it can make your image look squeezed and stretched. Usually these options are presented to the client one by one and we let them make the decision on site. It doesn’t take long for us to show each option using our video processor.
These concepts are also visited when putting video on a vertical LED column or horizontal LED ribbon. The main thing to remember is if the video is not specifically designed for the aspect ratio of the screen, then you will have to make concessions in losing the edges of the picture or squeezing the picture to fit, altering the image.
What is common cathode technology?
Common cathode is an aspect of LED technology that is a more efficient way of delivering power to the LED diodes. Common cathode gives the ability to control the voltage to each color of the LED diode (Red, Green and blue) individually so that you can create a more energy-efficient display, and also dissipate heat more evenly.
What is HDR ?
HDR: A More Realistic Way of Displaying Colors and Contrast HDR, or High Dynamic Range imaging, is a technique that allows digital devices to produce, transfer and display content with a much wider range of colors and contrast than before. A standard display (SDR) can only show 16.7 million colors, while an HDR display can show 1.07 billion colors. This means that HDR can display colors and details more accurately and vividly, as they appear in real life.
Newsletter
Subscribe today and get educated and entertained
with the monthly Visionpi Visual email Newsletter
