LED display packaging has developed from early-days DIP (dual in-line package) to today’s multiple packaging methods such as SMD, IMD, and COB,. These methods have reshaped the industry.
Definition of fine-pitch LED displays
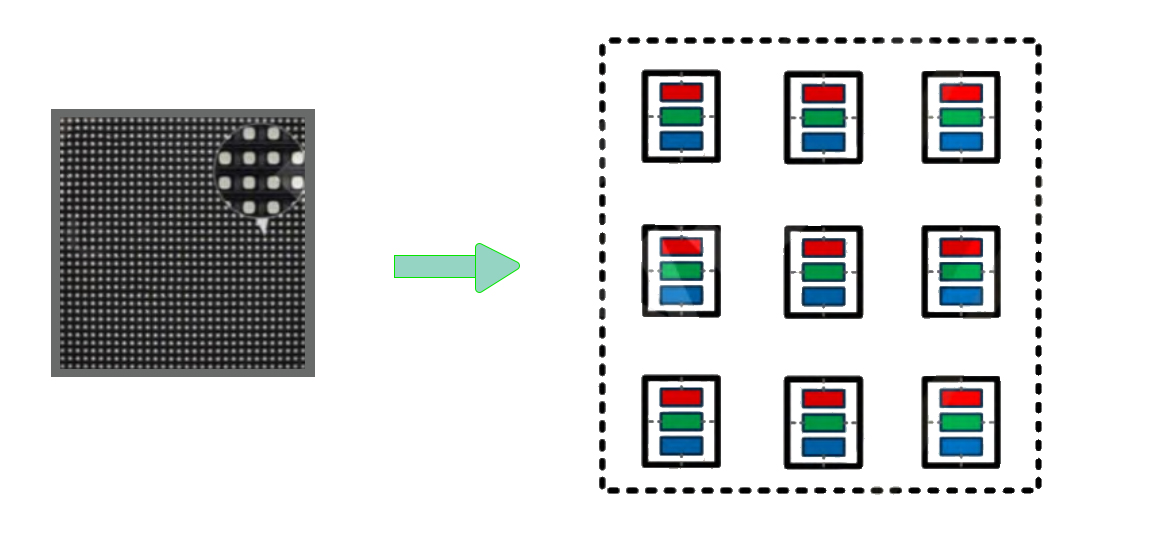
Fine-pitch LED display generally refers to LED displays with pixel pitch at or below 2.5mm. Mainstream fine-pitch LED display products are referred to as P2.5, P1.8, P1.5, P1.2, P0.9, etc. As technology develops and costs lower, direct-view fine-pitch LED displays are being used in an increasing number of applications, including corporate, retail, and educational settings, control rooms, broadcast studios, 3-D, and virtual or augmented reality displays. Compared with traditional larger-pitch LED displays, fine-pitch LED displays to bring higher resolution (full HD, 4K, 8K, and higher) to the application market, allowing an increasingly broader range of creativity. Fine-pitch LED display is a general term for a larger set of systems, consisting of LED display, HD/UHD display control systems, video processing systems, etc. Fine-pitch LED displays to use pixel-level point control technology to achieve a highly detailed level of brightness, color reproduction, and uniformity in every pixel unit. A key production link in the fine-pitch LED display manufacturing process is Automatic Reflow Welding, which helps to improve the reliability of welding and tremendously reduces the pixel failure rate.
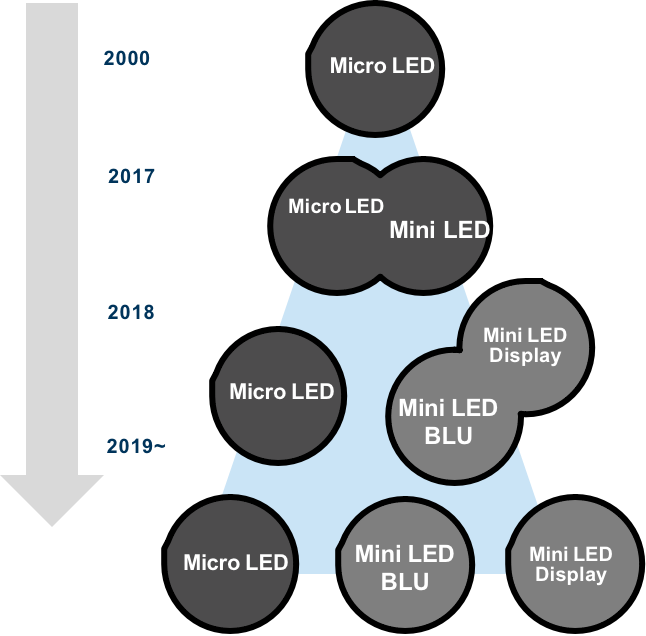
Development history of fine-pitch LED displays
Since LED displays entered the application market, they have developed from single- and dual-color displays to full-color screens, then to fine-pitch. Prior to 1993, LED display screens were limited to red and green dual-color displays and were used in limited applications such as traffic lights and the banking & securities industry. In 1993, Nakamura Shuji invented the blue LED chip, which completed the three primary colors (RGB) and opened a new chapter of full-color displays. In 2001, SMD packaging was introduced, and Chinese LED display manufacturers gradually grew in scale and expanded from domestic to overseas markets. By 2009, European and American enterprises withdrew from the LED display manufacturing market, and Chinese manufacturers became a driving force in the global LED display industry.
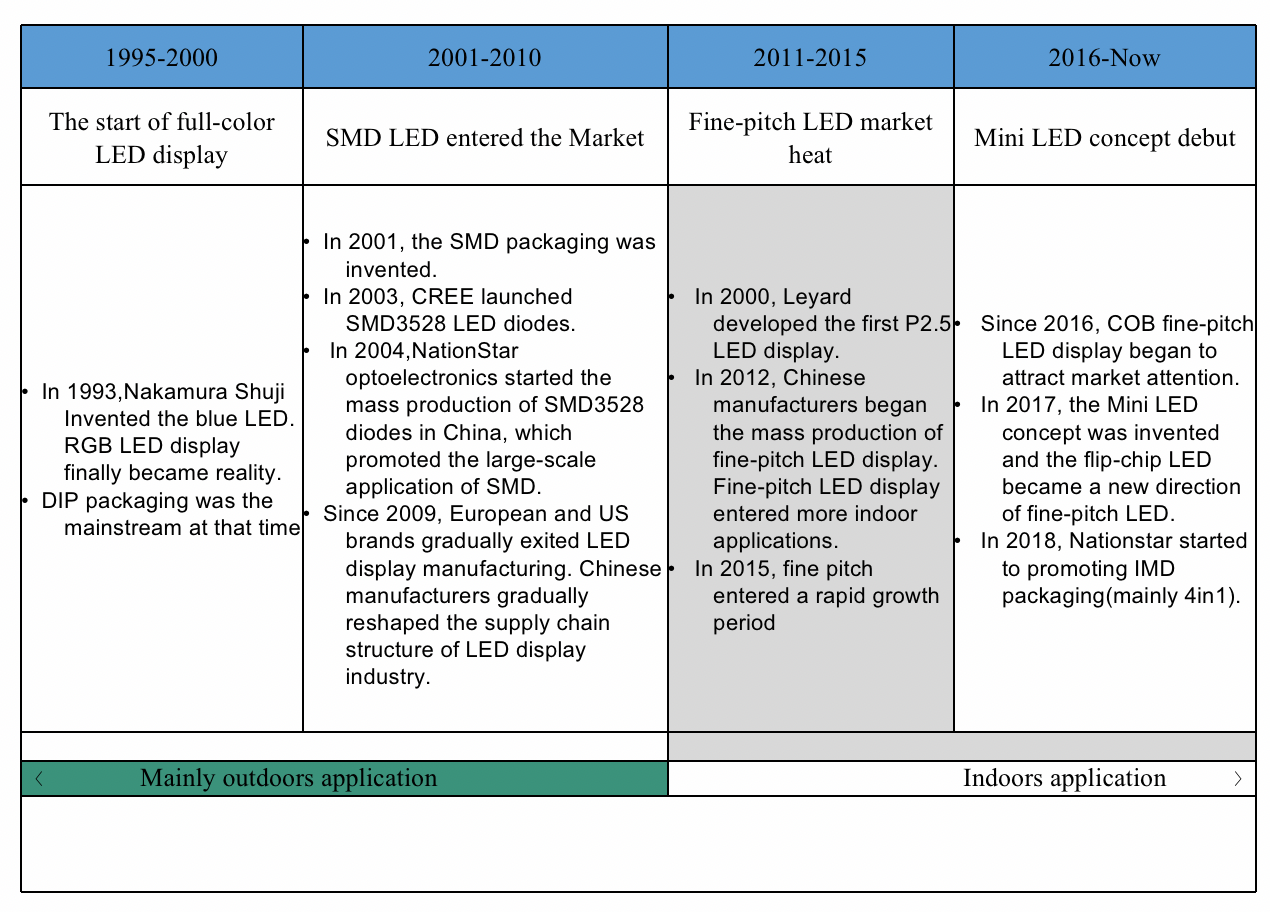
In 2010, with the launch of the first P2.5mm fine-pitch display, the entire industry began a long-term evolution from outdoor to indoor applications, shifting from larger to finer pitches. The following five years witnessed a stunning 3-digit growth rate with fine-pitch products used in more and more applications. In 2015, facing pressure from Chinese LED display manufacturers, whose compound annual growth rate exceeded 100%, manufacturers of traditional rear-projection and LCD equipment, such as Samsung, Panasonic, Planar, NEC, etc, also joined the fine pitch race. In 2016, Sony-made COB products caught market attention, especially after its Crystal Micro-LED screen, based on COB packaging technology, exhibited at CES in 2017. In the same year, the concept of mini-LED was raised and COB packaging further advanced to flip-chip technology. In 2017, IMD (integrated matrix device, also known as N-in-one) technology was introduced by NationStar with its pioneering product, the 4-in-1 IMD0.9, dividing the fine-pitch market into three major product lines: SMD, IMD, and COB.
2020 was expected to be the beginning of the Sub-1 mm Era, with a conservative estimate of 5% of overall fine-pitch sales volume. However, due to the worldwide outbreak of COVID-19, the Sub-1 mm Era may be postponed into 2021 or even 2022.
VISIONPI provides a full range of fine pixel pitch led wall solutions from 0.77 to 2.5mm.Get answers about Pricing, Specifications, Installation, and more.
