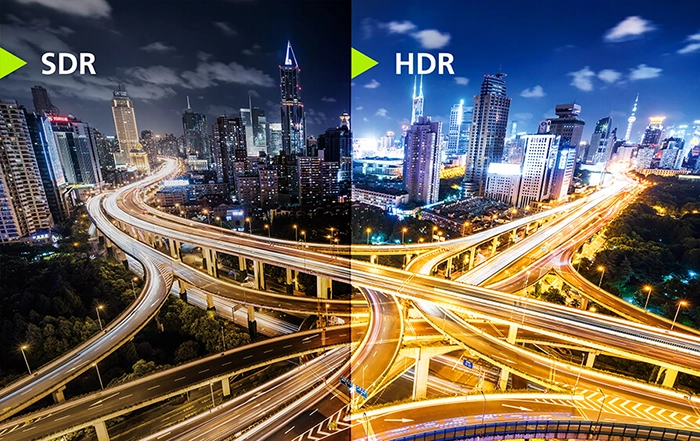
HDR stands for High Dynamic Range, which is a technique of capturing, processing and displaying images that have a much wider range of color and contrast than standard dynamic range (SDR) images. HDR images can show more details in both bright and dark areas, as well as more vivid colors, making them more realistic and closer to what the human eye can perceive. HDR is often used in photography, video games, movies and TV shows to enhance the visual quality and immersion of the content.

There are several HDR industry standards that define the technical specifications and requirements for HDR content creation and display. Some of the most common ones are:
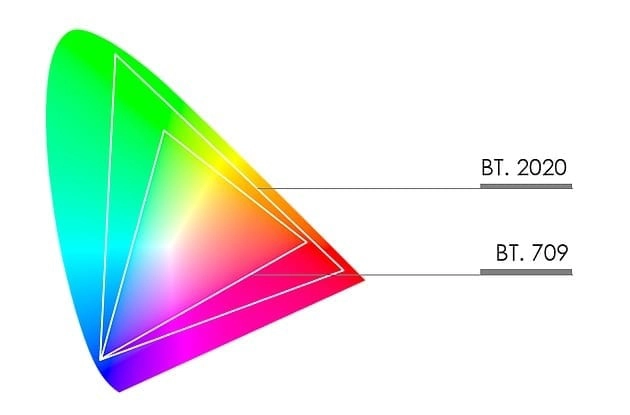
- HDR10: This is an open-source HDR standard that is widely supported by most HDR display devices and media platforms. It was announced by the Consumer Technology Association in 2015 and requires a 10-bit color depth, a BT.2020 color space, and a minimum display brightness of 1000 nits.
- HLG: This is a HDR standard developed by the BBC and NHK for digital program delivery. It was launched in 2015 and does not use metadata, but rather combines HDR signals into TV broadcast signals. It is compatible with current broadcast equipment and has no licensing fees. It is suitable for cable/satellite TV and live broadcast.
- Dolby Vision: This is a proprietary HDR standard developed by Dolby Laboratories that requires certification and payment. It was launched in 2014 and offers a 12-bit color depth, a BT.2020 color space, and a minimum display brightness of 4000 nits. It also uses dynamic metadata to optimize the HDR image quality for each scene. It is supported by some TV manufacturers such as Sony and LG.
Four requirements for HDR video to be realized, specifically for the HDR10 standard.
- 4K resolution, which means they have 3840 x 2160 pixels. This is four times more than the standard HD resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels. Having more pixels means having more clarity and sharpness in the image, which is essential for HDR.
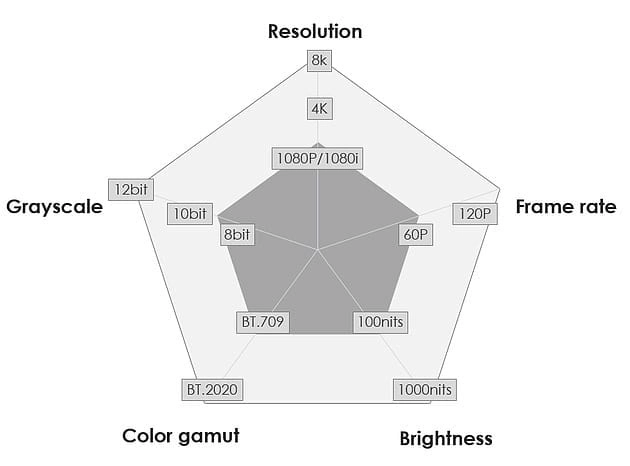
- High contrast ratio, which means it can show a big difference between the brightest and darkest parts of the image. For HDR10, the display device must be able to produce at least 1000 nits of brightness, which is a measure of how bright a screen can get. It must also be able to show blacks of less than 0.05 nits, which is a measure of how dark a screen can get. Having a high contrast ratio means having more details and depth in the image, which makes it more realistic and vivid. LED displays are very good at achieving high contrast ratios, unlike some other display technologies.

- 10-bit color depth, which means they can show 1024 shades of each of the three primary colors (red, green, blue). This is much more than the 8-bit color depth of standard video, which can only show 256 shades of each color. Having more shades of color means having more smoothness and richness in the image, which avoids the problem of “banding” or “stepping” between colors. It also means that some parts of the image can be very bright without affecting the rest of the image, such as the sun, a flash, or a fire.