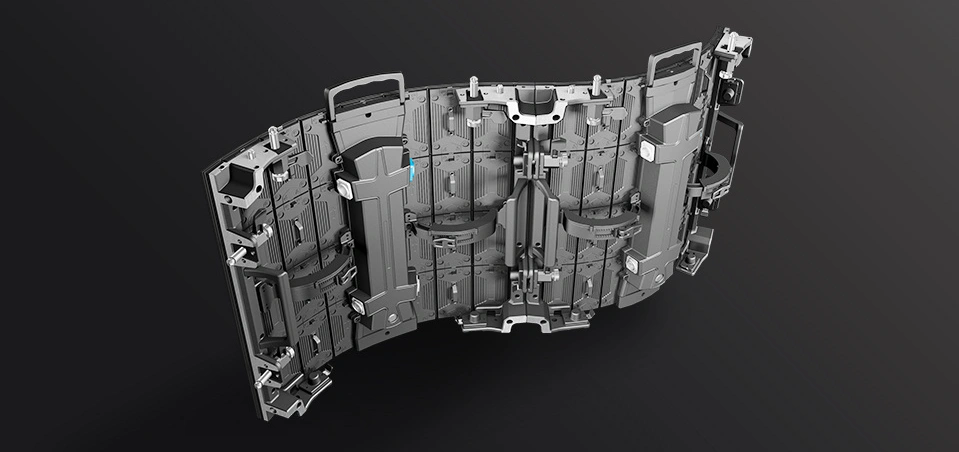
HOB LED Display
HOB VS GOB LED DISPLAY
What is GOB
To Understand what is HOB(HGOB) we need to learn what is GOB.
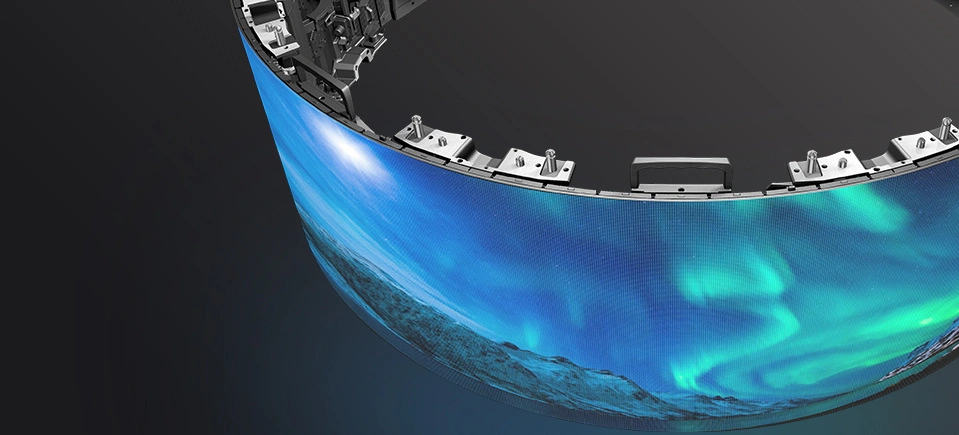
Glue on board is abbreviated as GOB. It is an epoxy resin that is applied to the surface of surface-mounted display modules to create an overall layer of glue that improves the sealing of SMD displays. It is a technology developed to address the issue of LED lamp protection. GOB LED Display is able to work in any challenging environment, making it water-resistant, dust-proof, shock-resistant, and UV-resistant, it is widely used in restaurants, hotels, bars, and Stadio.
What is HOB?
HOB (Hotmet on Board) is a process that uses nanomaterials with high refractive index to coat the surface of the screen and form a protective layer that covers the LED chips completely. This layer prevents the LED chips from being affected by external factors and increases their stability and lifespan. It also improves the quality and efficiency of the LED displays during the packaging process.
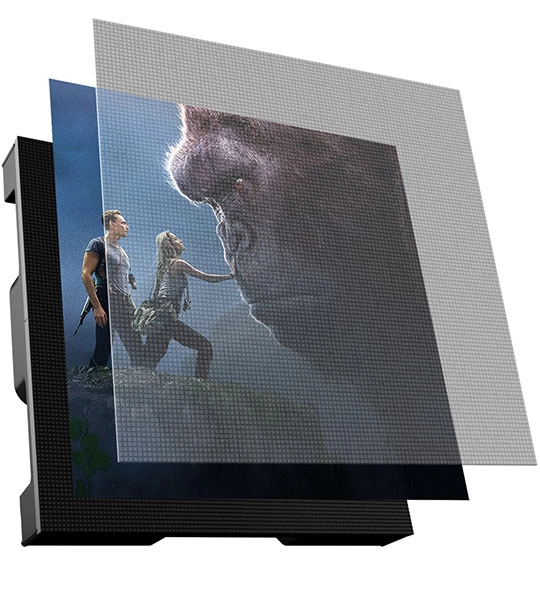


GOB VS HOB
HOB uses a high-temperature molding process, while GOB uses a normal-temperature dispensing process. HOB has better thermal stability, accuracy, flatness, and thickness control than GOB. Moreover, high-temperature molding can prevent the glue from cracking due to heat generation during LED operation.
Durability
HOB adopts the COB process of high-temperature molding with a polymer synthetic colloid, which contains various additives, coagulants, and anti-UV agents. This can prevent the yellowing problem of ordinary epoxy, and also adjust the black pigment and design the mold frosted surface.
Anti-Scratch.
When you place a conventional GOB product and a HOB product side by side, and scratch the surface with a screwdriver, you will see a clear difference. The GOB product is not scratch-resistant and will show scratches and cracks immediately, while the HOB product will remain intact. This is because the HOB product uses the COB process of high-temperature molding with a polymer synthetic colloid, which has various additives, coagulants, and anti-UV agents. This can avoid the yellowing problem of common epoxy, and also modify the black pigment and create the mold frosted surface.

Optical performance
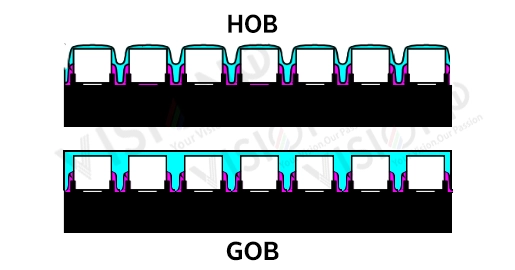
GOB process has a variable thickness of the final product, and a difference in the flatness of the self-leveling colloid, which results in a thicker GOB product. This causes a more noticeable edge refraction problem when splicing on a large scale, which is commonly known as the bright line problem of the writing angle.
HCOB uses precision molding tools, which ensure that its thickness is only up to 0.2mm higher than the LED height, and the light hardly undergoes secondary refraction at the edge of the colloid.
Contrast
The surface of the final product of the ordinary GOB process is a mirror surface, which cannot achieve a frosted or matte surface.
HCOB uses mold design and pressure molding to create a frosted surface, which is similar to matte black light. This increases the contrast of the entire screen by 40%.

Precision
HCOB uses high-precision mold technology, which allows the overall molding accuracy to be controlled within 0.2mm, according to conventional mold precision. GOB uses room temperature molding, which depends on the molecular internal coagulation curing, and has a shrinkage problem. The best progress of GOB so far is 0.5mm, and some products need secondary processing. HCOB technology has been applied in batches on the mainstream pitches of 1.2, 1.5, and 1.8.