LED Display White Paper

Why this guide?
Understand the industry
Understand the specification and get what you want

Accurate information matters
Contact us for a 33 pages free copy white paper


Accurate information matters
Contact us for a 33 pages free copy white paper
LED PIXEL PITCH
To learn what pixel pitch is and why it matters, you first have to know what a pixel is. You may think you already know what a pixel is, but a lot of people find out there’s more to the “pixel” than they originally thought. A pixel is a cluster of colored light sources, and this cluster almost always contains at least one red, green, and blue light source
Many people mistakingly think that each little “light” or diode is a pixel. The full pixel is the entire cluster of the red, green, and blue lights. Pixels can be in a triangle pattern as seen here:
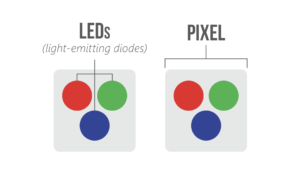
Pixels can also be very tightly arranged in a small SMD’s. SMD stands for Surface Mount Diode. Each little SMD you see in this picture has very tiny red, green, and blue light sources inside each one. SMD’s are now almost universally used for new high resolution LED screens.

Now that you know what a pixel is, let’s talk about why it matters. Pixel pitch is the distance from one pixel to the next pixel beside it, above it, and below it. So, if your entire LED wall is said to have a 10mm pixel pitch, then that means there is 10mm of space from the center of one pixel (red, green, blue diode cluster) to the center of it’s neighboring pixel. Which, in quick American conversion, is 3/8 of an inch. As you can imagine, the smaller the pixel pitch, the tighter the resolution or the closer you can be to the screen before you can make out individual diodes in the image.
Now that you know what pixel pitch is, here’s quick way to start thinking about what pixel pitch would be right for your LED screen. Take the distance that your closest audience will be from the screen, in feet, remembering to account for height distance as well, then half that number and that should give you a good estimate of the pixel pitch range you should be looking at. For example, if your closest viewer is going to be 20 feet away from the screen, then you should be looking in the 10mm or lower set of products to ensure that even the closest audience member will see a nice, clean, blended picture with little to no pixelation. Remember, all you have to do is half the distance in feet from your closest viewer and that’s your ideal pixel pitch. If your closest viewer will get no closer than 40 feet from your video wall, you can even use 16mm or 20mm pixel pitch and still get a great looking picture.
An IP rating is a way of indicating how well an enclosure or device protects against the ingress of solid and liquid objects. IP stands for Ingress Protection, and it is followed by two digits that represent the level of protection against different types of objects. The higher the number, the better the protection. Sometimes, a digit is replaced by an X, which means that the enclosure or device is not rated for that type of object.
The two digits in an IP rating have different meanings. The first digit indicates the level of protection against solid objects, such as dust, sand, or dirt. The second digit indicates the level of protection against liquid objects, such as water, oil, or steam. Here is a table that summarizes the meaning of each digit:
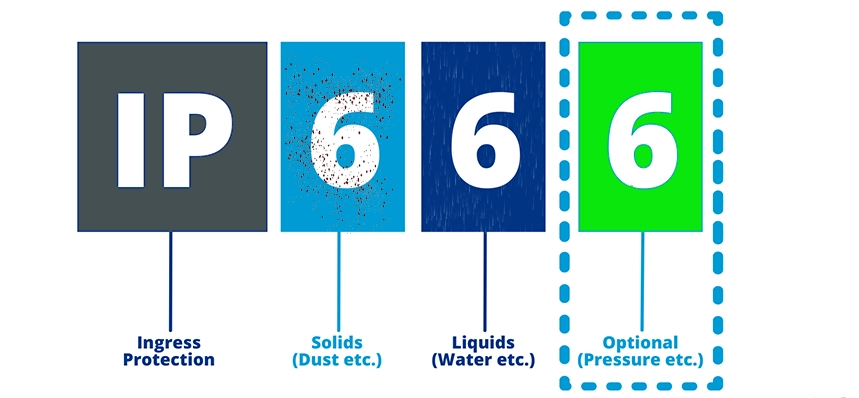
For example, an IP rating of IP68 means that the enclosure or device is dust-tight and can withstand continuous immersion in water under specified conditions. An IP rating of IPX7 means that the enclosure or device is not rated for solid objects, but can resist water immersion up to 1 meter deep for 30 minutes. An IP rating of IP4X means that the enclosure or device is protected against objects larger than 1 mm in diameter, but not rated for liquid objects.
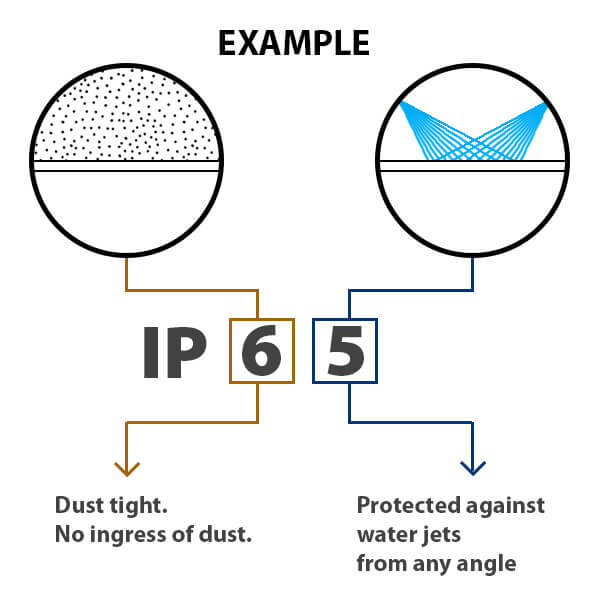
IP ratings on LED displays are a way of measuring how well they can resist dust, water, and other environmental factors. They are important because they help you choose the right product for your needs, whether it is indoor or outdoor, permanent or temporary, humid or dry.
For outdoor LED displays, you should look for a minimum rating of IP65 at the front and IP54 at the back if you are using them for short-term applications, such as rental and staging. This will ensure that the display can handle rain, wind, and dust. If you are installing them permanently, you should look for a minimum rating of IP65 for both the front and the back. In some case IP67/IP68 is required especially if the display is exposed to harsh weather conditions like desert and coastal area ,swimming pool ect.

IP65 means that the product is dust-tight and can withstand water jets from any direction. This is suitable for most outdoor products that are not exposed to extreme weather conditions.
IP67 means that the product is dust-tight and can withstand temporary immersion in water up to 1 meter. This is suitable for products that may be submerged in water occasionally, such as underwater cameras or smartwatches.
IP68 means that the product is dust-tight and can withstand continuous immersion in water beyond 1 meter. This is suitable for products that are designed to operate underwater, such as diving equipment or marine sensors.


For indoor LED displays, the IP rating should match the installation environment. If the environment is relatively neutral, such as an office or a classroom, a low IP rating of IP20 or IP40 (SMD LED DISPLAY)may be sufficient. However, if the environment is high humidity or dust-prone, such as a swimming pool or a factory, a higher IP rating of IP54 (COB LED DISPLAY or GOB LED DISPLAY)or IP65 may be better. A higher IP rating can prevent moisture and dust from damaging the LED display and causing operation issues.
IP rating is a way of indicating how well-LED screens can resist dust, water, and other environmental factors. It is important to choose an LED screen with the right IP rating for your needs, as it can affect the quality and durability of the product. Some products may claim to be waterproof without any IP code or standard to back it up, but this may be a marketing strategy to attract customers. Therefore, you should be a smart consumer and trust IP rating more than mere words.
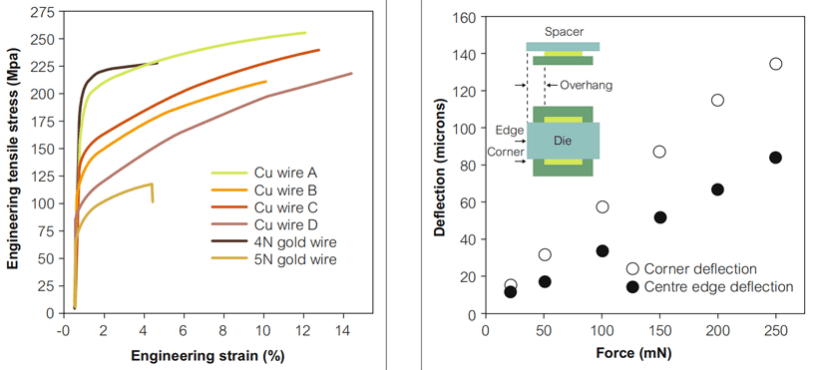
The conductor and wire bonding in the package is the apparatus that transfers electric current from the circuit board to the diodes. Conductors are located on the underneath or back side of the package carrier and consist of an anode and cathode division (positively and negatively charged). These pieces are manufactured from one of three different metals – Gold, Copper, silver, or even Iron. Copper Wire bonding refers to the wire bonding process that employs copper wires for interconnection, instead of the gold and aluminum wires traditionally used in semiconductor packaging.
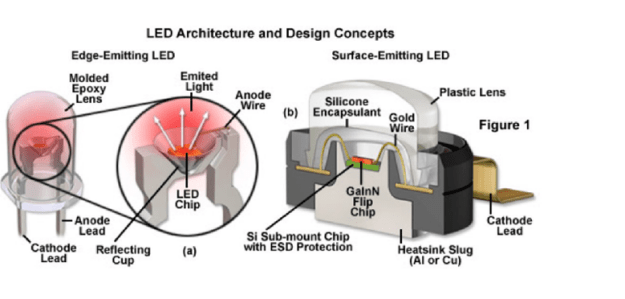
There are variances in both conductivity and environmental performance with these three metals.
Gold is the preferred metal for both situations, having both the best conductivity and being the most environmentally resistant – but as expected it is also the most expensive.
Silver/ Iron is the most susceptible to corrosion and Copper is not gold and it is unreasonable, given the different physical and chemical characteristics of each metal, to expect copper simply to bond in the same way as gold. From a performance point of view, copper can be as reliable as gold wire but copper is facing problems in more challenging stress tests such as temperature cycling, If you are in an indoor environment naturally this isn’t usually a concern with controlled, low-humidity.
For this moment, gold wire still is the more stable one for the LED display. While larger-diameter copper wire has been utilized in many applications for some considerable time, the copper bonding wire is not a ‘drop-in’ solution for gold wire and should not be seen as such in fine and ultra-fine pitch applications. Copper wire from different suppliers can differ considerably in purity and mechanical properties during the process. That is why, for small pixel pitch, normally Gold wire is adapted.
Copper VS Gold Copper Wire bonding refers to the wire bonding process that employs copper wires for interconnection, instead of the gold and aluminum wires traditionally used in semiconductor packaging. Copper is rapidly gaining a foothold as an interconnection material in semiconductor packaging because of its obvious advantages over gold. These advantages include:
A. ReeStar ™ (“RS”), a high-end full-color display device launched in 2013, mainly has four models, is a high-end brand of indoor foreign star high quality LED screen, more than three years warranty, excellent performance can fully realize the led high-definition display, high contrast ratio, high waterproof, high reliability, low light decay and other requirements. requirements.
B. 7 Major Performance Advantages of RS
• a). Waterproof and moisture-proof: waterproof performance reaches IPX8 level; moisture-proof performance reaches MSL 2a level.
• b). Cold and thermal shock resistance: high bonding of packaging materials, -65℃~+150℃ cold and thermal shock without dead light.
• c). Anti-back pressure: meet the high refresh frequency demand, 85 ℃, 85% RH, simulated back pressure test without failure.
• d). Salt spray resistance: the use of a wide range of simulated seaside corrosive environment without dead lights.
• e). UV resistance: UV experiments accelerated aging outdoor simulation using 3 years, light decay is less than 20%.
• f). Low light decay: high temperature and high humidity accelerated aging simulation of outdoor use for 3 years, light decay <20%.
• g). High brightness: the highest brightness level in the industry.
C. RS’s 3 Major Appearance Advantages
• a). Matte surface, high contrast.
• b). Surface luminescence technology: turn point into surface, solve the problem of led glare.
• c). Low pin technology: high cup and short foot, easy for customers to fill glue and cover mask.
D. There Are 4 Main Models
RS-1921MBAR, RS-2020MBAM, RS-2727MWAS, RS-3535MWAR

Copper is inherently 2 to 5 times cheaper than gold, so substituting gold wires with copper wires can realize tremendous annual cost savings for a semiconductor packaging company:
let’s do simple math, you will see how much difference in price among those LED of varied bonding material: For example: P10, 10,000 Pixels/sqm with Nationstar LED 3535: Gold wire: High brightness: 20USD/K Copper Wire: Normal brightness: 10 USD/K Iron Wire: 5USD/K So Basically you can see the price difference, gold wire is about twice of copper. When it comes to indoor LED with a smaller pixel, the price can be a huge difference. if you see P2 (250,000 pixels/sqm),nationstar gold wire 1010 is roughly 8 USD/K.while copper wire is 4 USD/K. so it is about 1000 USD more. Most of the time factories /salespeople won’t tell you about the wire bonding material, unless you ask, even you ask, they can lie, because this no way you can recognize the difference by your eyes. except for chemical lab testing. Visionpi has a long term partnership with Nationstar/Kinglight, we provide verification service to our customers.
copper and gold wire bonding are both widely used techniques for connecting LED chips to external circuits in the LED video display industry. Copper and gold wire bonding have distinct advantages and disadvantages based on their intended use. Copper wire bonding is an economical choice that offers high thermal conductivity but has limited lifespan and low electrical conductivity. On the other hand, gold wire bonding, which is more expensive, provides thin wires and high electrical conductivity while having low thermal conductivity. Ultimately, selecting between copper and gold wire bonding should be based on the specific needs and requirements of your LED video display project.
Accurate information is the key to evaluating the quality and performance of any manufacturer’s LED DISPLAY. However, there are some manufacturers, who produce and sell LED MODULES in a large quantity, and they usually sell to other LED factories/companies.they are using mainly are iron wire bonding led (Mulinseng, HongSeng), for price sake. The competition is getting fiercer, there are small companies who sell inferior quality LED but claim to be a good one. Even now you know those brands and quality level. but you are unable to tell if it is real. After a few months running, the display will bleed you on the maintenance cost. Visionpi provides LED verification services, we can be your professional QC team to help you with the sourcing and inspection and bring lower purchase cost and guaranteed quality.check more our services.
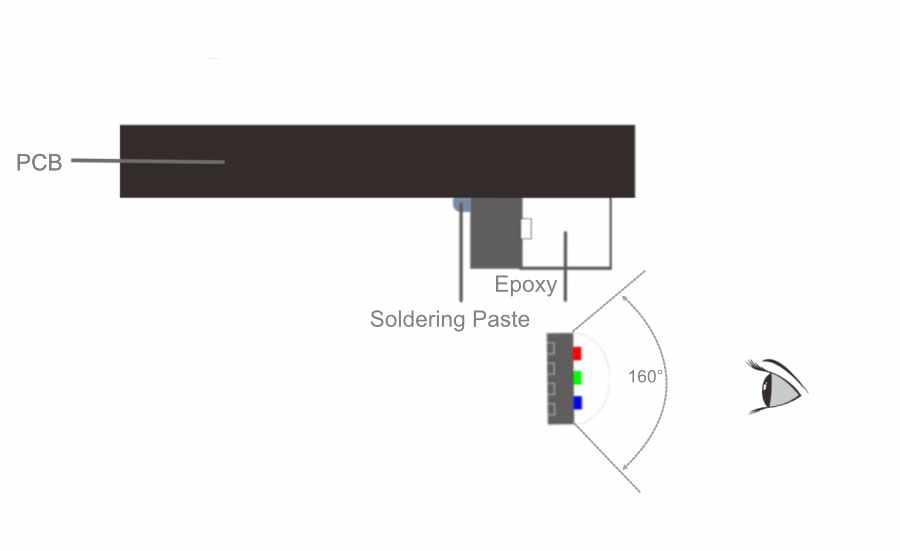
Side-emitting LED: It is a solution adopted by some professional transparent screen manufacturers to adopt Side-emitting LED lamp beads specially tailored for LED transparent screens. It is characterized by high permeability, less structural span, and good aesthetics, and is conducive to large-scale standardized production of LED screen factories.
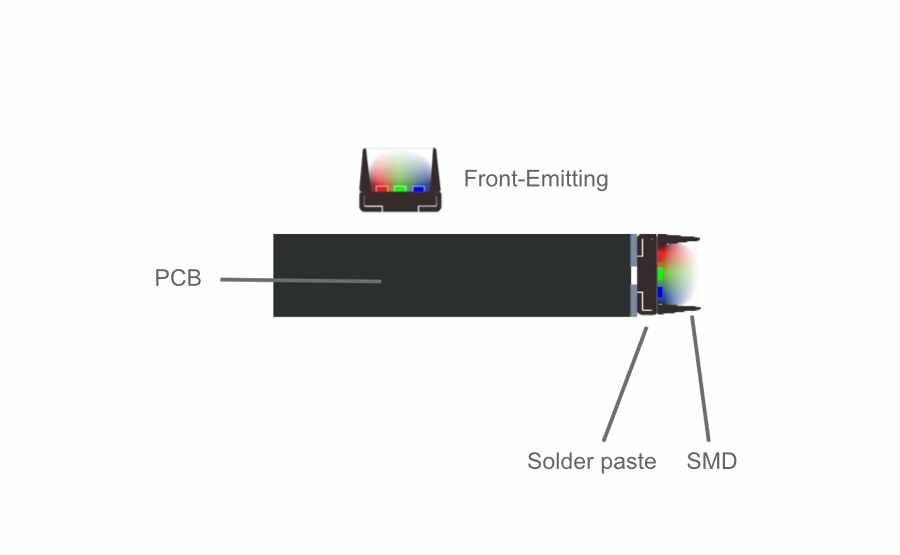
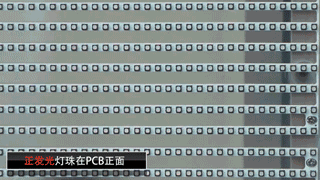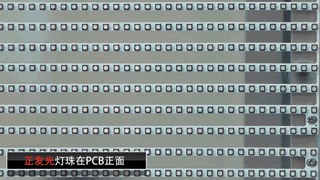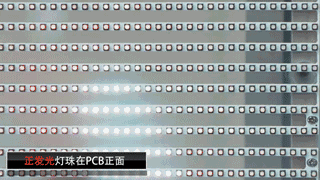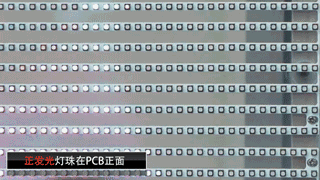

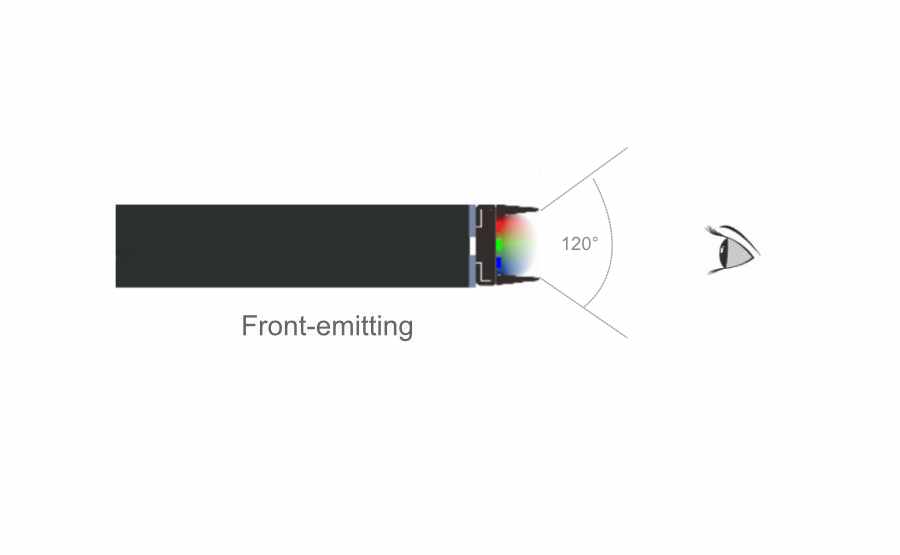
Front-emitting LED: Most transparent screen manufacturers use the conventional package lamp beads in the market. The screen’s permeability is relatively low, the price is low, and the structural span is more, which affects the aesthetics.
Due to the different placement of the lamp bead, the thickness of the lamp strip of the Front-emitting LED transparent screen must be larger than the size of the lamp bead, while the placement and space of the Side-emitting LED lamp bead are less limited. Because the light bar itself blocks the light, the permeability of the Side-emitting LED transparent screen is better than that of the Front-emitting LED screen. This is the most obvious advantage of the Side-emitting LED transparent screen.
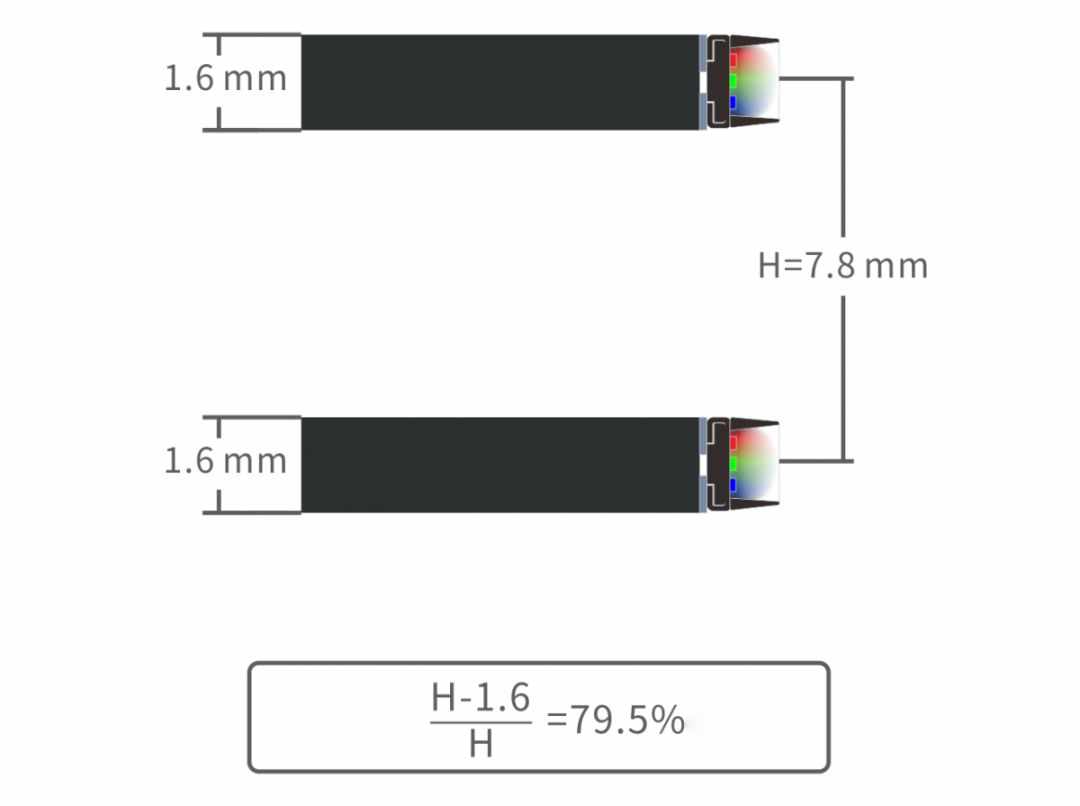
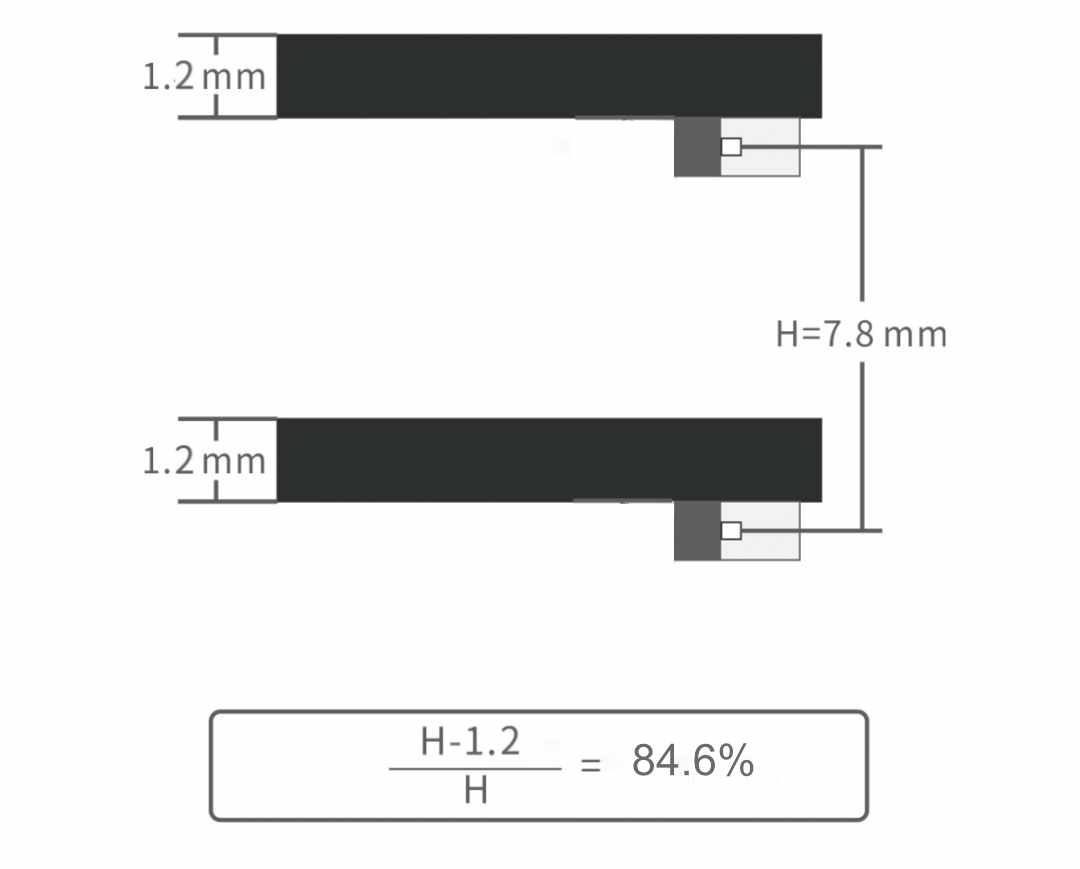
Because the bead is placed in different places, the two screens differ in their ability to prevent collisions. Under the impact of external forces, the Front-emitting LED will directly receive the impact of external forces, and the Side-emitting will not be directly stressed.
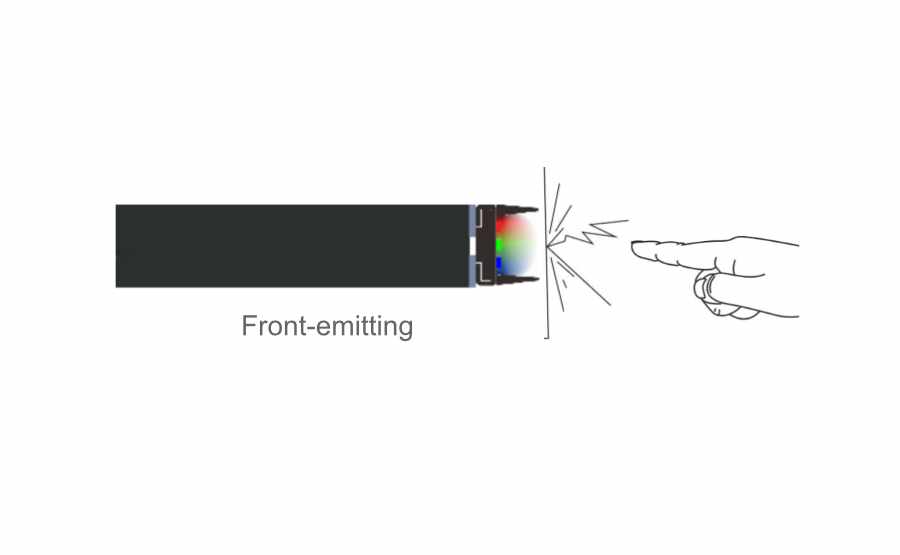
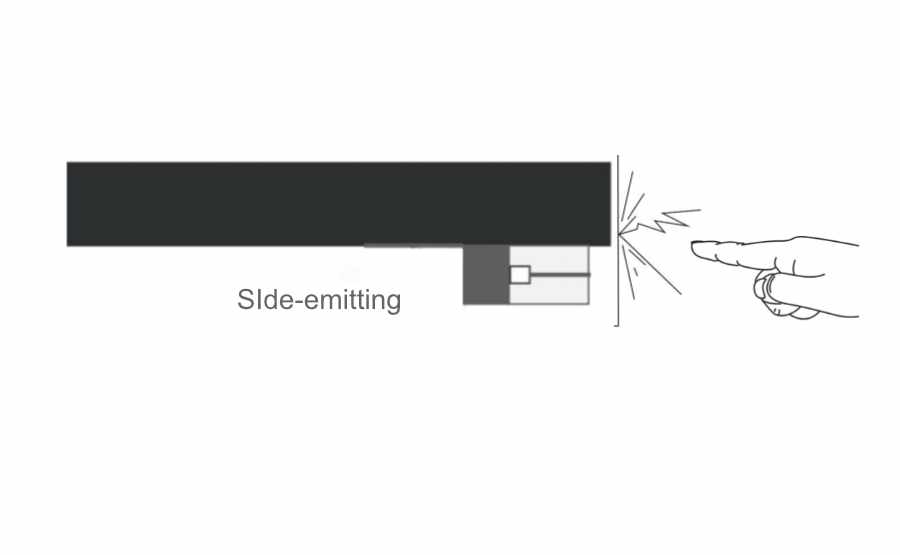
Viewing angle: side-emitting led :over 160° front-emitting led 120°
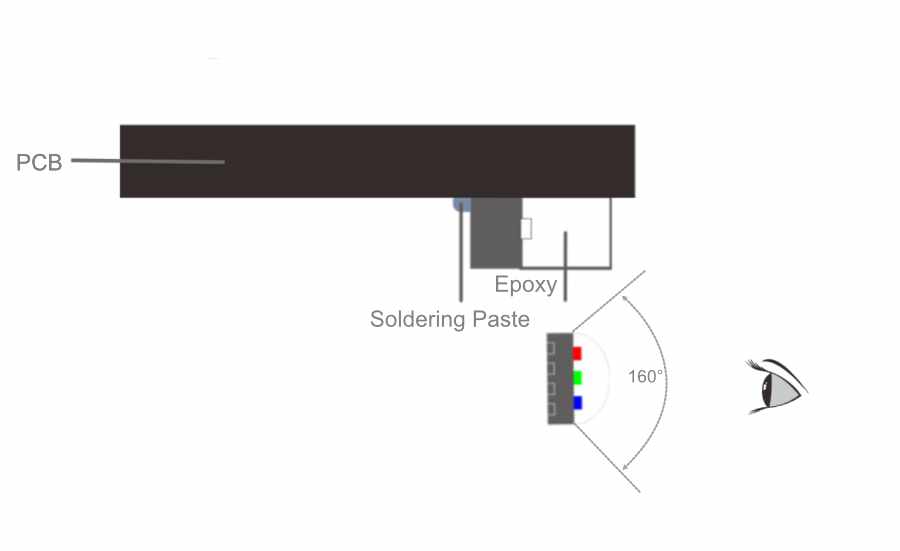
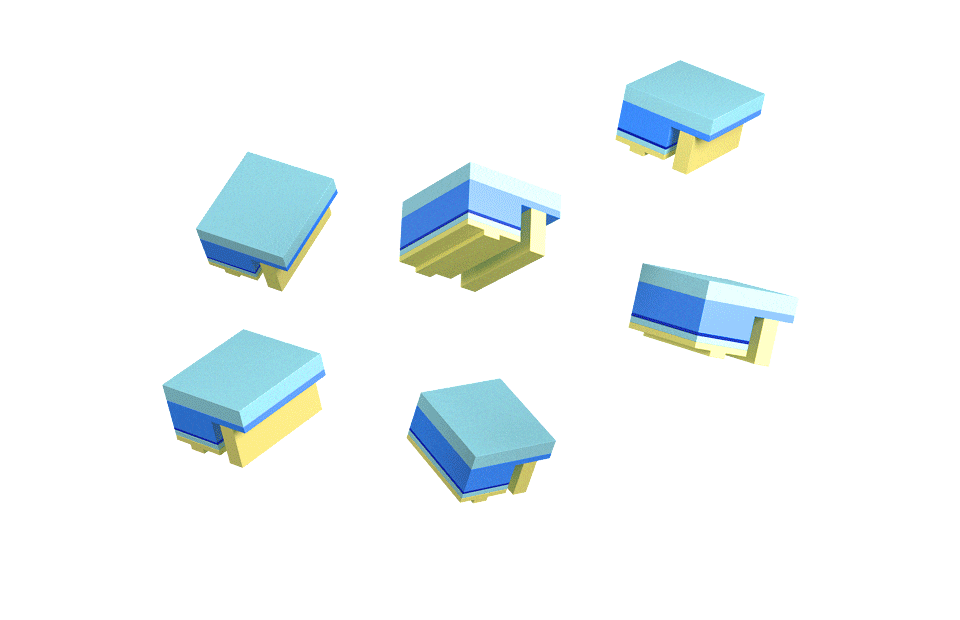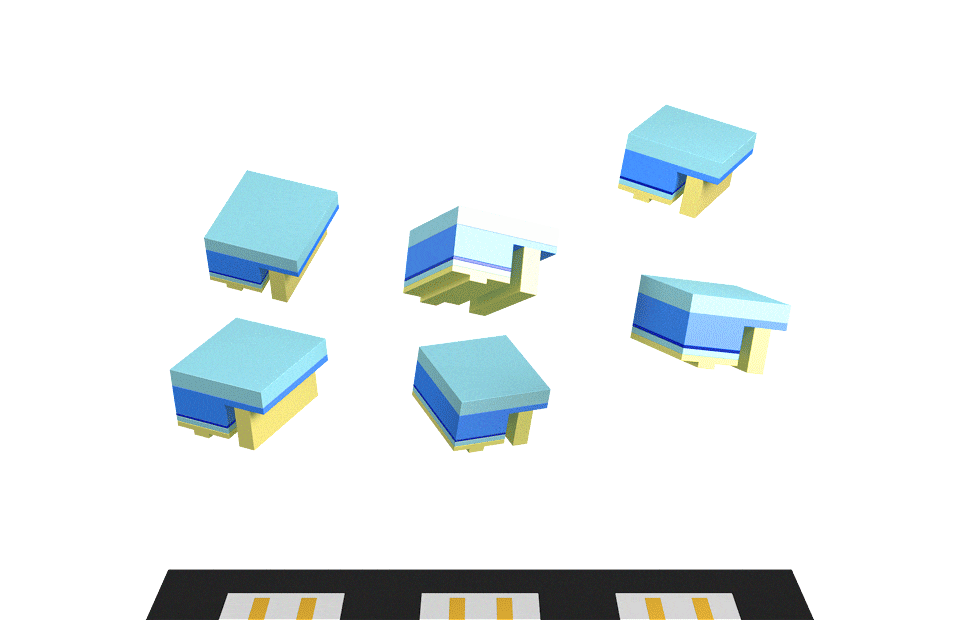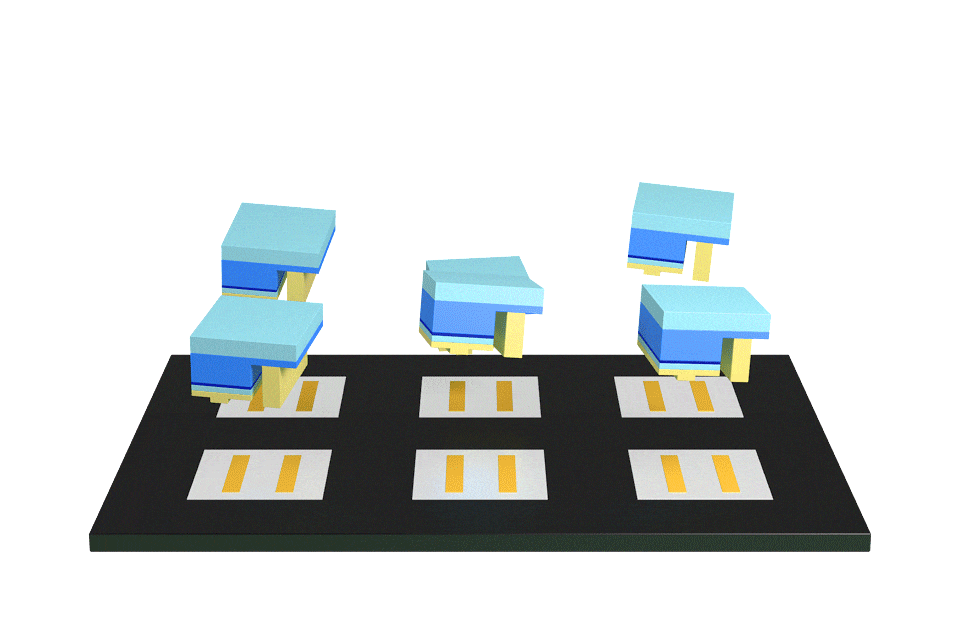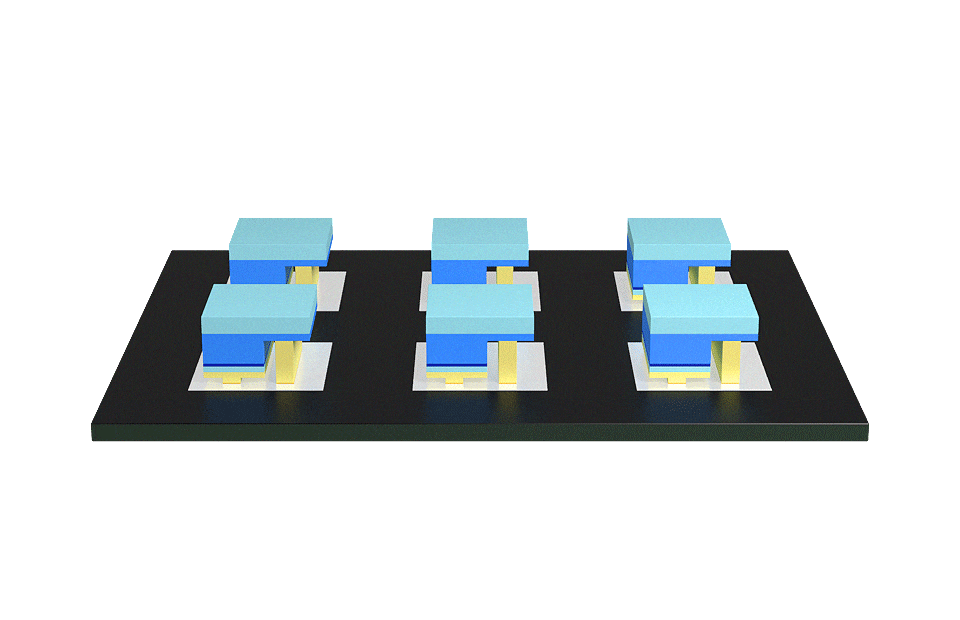
The bare IC is mounted directly on the substrate on the back of the PCB, then using a special method of welding using a pure gold wire, a bond is made between the base and silicon chip, then finally the COB is packaged together to form the full-color module.
Micro-led Mass Transfer Technology
Mass transfer is a technique that can move Micro-LED chips from wafers to display panels.
This is the most challenging part of making MicroLED displays. There are three main challenges in this step “ accuracy, speed, and reliability.
The transfer process requires high accuracy, as each microLED chip is minuscule and has to align precisely with its designated location. The tolerance for deviation is very low.
The transfer process also requires high speed, as contemporary displays have very high resolutions. For instance, a 4K display comprises more than 24 million subpixels. To achieve cost-effectiveness and productivity, the transfer process has to handle multiple microLED chips simultaneously.
The transfer process also requires high reliability, as the display industry expects high standards and low defects. As the displays become larger and finer, the quality becomes more critical. We will elaborate on the microLED quality issue in a subsequent section.
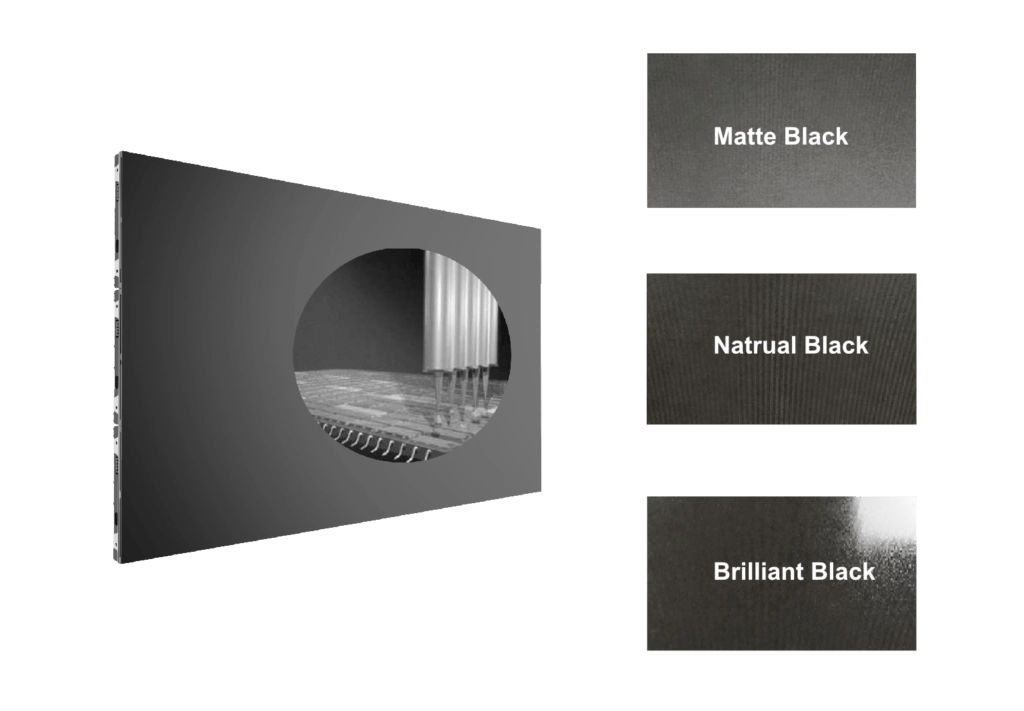
Flip Chip COB series micro & mini LED display provides three types of surface treatments, including Brilliant Black, Natural Black, and Matte Black.
This new and unique technology has a number of advantages over existing technologies such as SMD and DIP LEDs. Due to the small size of the LED chip, the COB system allows for a much higher packing density than SMD (SMT), the result being a more compact array giving better uniformity and higher intensity even at a close distance and greater heat dissipation for better stability, reliability, and lifespan.: COB chip and pin legs are sealed, resulting in better airtightness, higher resistance to external forces, and a smoother, seamless surface. COB has a much higher level of protection against moisture, electrostatic discharge (ESD), damages, and dust with surface protection rated IP65. COB is an integrated package with even light distribution, and the smooth surface makes images appear softer and friendlier to the human eye.



 Superior Durability COB is better at withstanding collisions and the effects of Oil, Damp, Water, Dust, Oxidisation, and dust.
Superior Durability COB is better at withstanding collisions and the effects of Oil, Damp, Water, Dust, Oxidisation, and dust.

When an LED display is encapsulated in COB, it must be ensured that the lamp is free of defects before refilling. Unlike an SMD package, a single bulb cannot be replaced, so the packaging process is very demanding. (Visionpi’s patented mass transfer technique is a novel approach for transferring millions of micro LED chips accurately. With the mass transfer technology, the UPH of micro & mini LED displays is more than 2.5KK, and the mass production yield rate is more than 99.999%.)
if it is a traditional SMD package, you can disassemble the unit board after a single LED soldering repair. However, when it comes to the COB product, maintenance will affect the surrounding lamps, making it very difficult. Although its protection performance is better, we have to admit that there will still be a certain dead light rate. In this case, the only option is to replace the unit board. generally speacking the cost of maintenance is bout the same with SMD.COB panel is more expensive but with much less possibility of failures. as the cob manufacturing cost is decreasing, now the cob led display’price is very clost to SMD’s, in the future the cost will be lower than SMD.
LC-COB and FC-COB are two types of LED packaging technologies used in Chip-on-Board displays.
LC-COB (wire bonding) has LED chips mounted in parallel on the substrate with electrical connections made from the side of the chip. The chip is attached to the board with an adhesive. Each pad on the device is connected with a fine wire lead that is welded to the pad and to the circuit board. the wire lead would limit the development of finer pixel pitch led display.
FC-COB, on the other hand, has LED chips mounted upside down on the substrate with electrical contacts facing downwards. flip chip COB eliminates wire bonding and simplifies the production process.
Conductive adhesive bonds the chips to the substrate for better thermal and electrical performance.
A reflective layer on the substrate directs light emitted from the LED chips toward the front of the display, providing high brightness.
The flip chip takes a smaller space on the PCB board, providing a larger light-emitting area. The substrate presents a darker black field and higher contrast
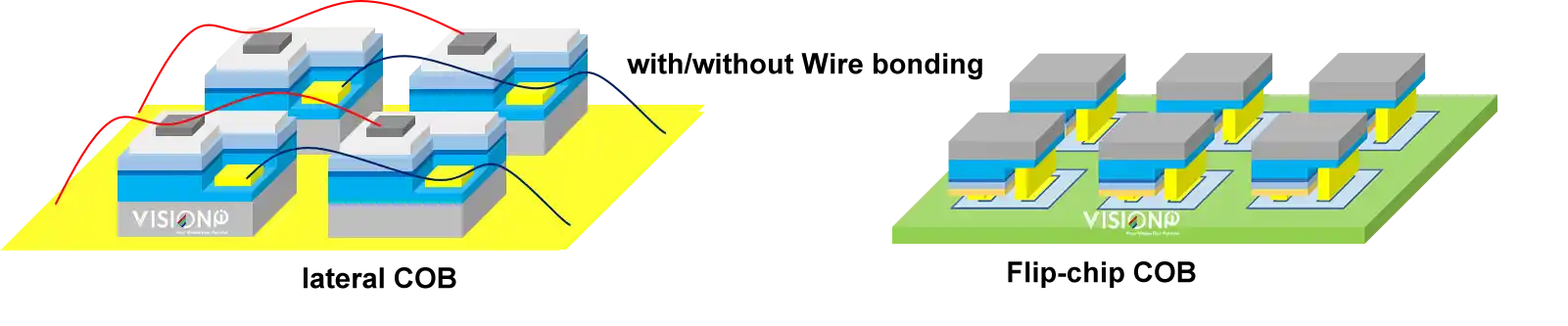
Flip-chip COB is the future. Compared with the SMD; GOB Packing technology (GOB VS COB), COB is the next-generation technology advance in COB that improves display quality and durability. It makes the pixels closer, brighter, and more visible from different angles and distances. It also makes the display more reliable, energy-efficient, and resistant to dust, moisture, and collision.COB LED displays are still a popular choice for a wide range of applications such as indoor and outdoor advertising displays, stage backdrops, and event screens, due to their high-quality visuals, energy efficiency, and durability.. In short, COB LED screen technology is a future development trend,the cost will be decreased with the mass transfter technology’s development.
We are a reliable display supplier that offers Mini COB LED displays with three advantages:
Pixel pitch covers P0.4-P1.8 to meet different requirements of users
Quantum Dot COB LED Displays: Revolutionizing Micro-LED Technology
Pixel pitch covers P0.4-P1.8 to meet different requirements of users
COB flexible LED modules merge the compact, high-intensity lighting benefits of Chip On Board (COB) technology with the adaptable, bendable nature of flexible LED modules. This innovative combination allows for the creation of highly durable, uniformly lit, and versatile lighting solutions that can be tailored to fit curved and irregular surfaces without compromising on light quality or intensity.

Our flexible COB LED display achieves seamless alignment through a CNC die-cast aluminum cabinet, ensuring high precision and uniformity. The die-casting process provides superior dimensional accuracy and stability, crucial for maintaining flatness in fine-pitch displays. It also minimizes pixel misalignment by maintaining consistent cabinet dimensions.
Additionally, aluminum’s excellent thermal conductivity aids in heat dissipation for high-density LED configurations, extending the display’s lifespan. The robust construction of the die-cast aluminum cabinet enhances durability and resistance to physical stress, making it suitable for various installation environments.
Explore VisionPi’s COB LED Display Module, the pinnacle of cutting-edge technology for OEM applications. As a leading manufacturer, VisionPi offers robust, high-density COB (Chip On Board) LED displays, perfect for creating seamless, high-resolution screens with exceptional durability and performance. Ideal for a wide range of applications from digital signage to sophisticated video walls, discover how our COB LED modules can transform your visual presentations into captivating experiences. Dive into the future of displays with VisionPi’s reliable and innovative solutions
Common cathode low power consuption and high brightness 1500nits cob led modules.